Bittensor Review: Has the Synergy of Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence Arrived?

ChatGPT, the initial large-scale AI product, has transformed the lives of millions, creating a distinction between the time before and after its introduction. This solution has strongly affected various fields and activities, notably the cryptocurrency industry.
In 2023, people got excited about ChatGPT. This led to the emergence of many ventures in the cryptocurrency market. These startups aimed to merge AI with blockchain technology. While most of these startups ride the hype wave, integrating decentralized networks and artificial intelligence holds the potential to address various critical technological challenges in the crypto space.
This article will analyze Bittensor, a prominent blockchain solution for AI.
What is Bittensor
Bittensor is a project by The Opentensor Foundation. It uses blockchain technology to create a peer-to-peer marketplace, improving AI model training efficiency. The product creates a decentralized infrastructure for monetizing algorithms and facilitating their data exchange.
The Bittensor team aims to overcome obstacles hindering the progress of the AI industry:
- specialization: AI models currently specialize in specific tasks, like generating images or text responses. This makes it hard for developers. They face competition and code closure, making it challenging to integrate various solutions into a single product;
- low learning efficiency: vendors use closed-source code and keep their AI models’ technical aspects confidential. This means each vendor has to retrain their algorithm. It’s to do functions their competitors can already perform.
As a result, businesses must invest in capacity and acquire vast data access. This consumes valuable resources, keeping pace with advanced algorithms. This lowers development efficiency and obstructs the general progress of the technology;
- monopoly: tech giants like OpenAI, Amazon, and Microsoft mainly develop several AI-based products. Among these products, GPT-4 is the most extensively used. It is a big language model used as the foundation for ChatGPT and various commercial solutions in websites, games, and other projects.
The increasing integration of artificial intelligence into different aspects of life raises concerns about a ‘single point of failure’ and possible restrictions on technology access upon regulatory requests. To tackle these concerns, one may implement a decentralized market model.
Bittensor has come up with the idea of an ‘AI marketplace’ to address these challenges. This platform has specialized algorithms that cater to particular tasks. It lets users choose the best solution for their needs. Providers earn compensation for sharing their expertise.
Users and software developers can use an infrastructure with AI models. It helps create applications like virtual conversationalists and image generators. The Bittensor network provides several request-processing services, including:
- TAO Studio – an algorithm that generates images based on textual prompts;
- ChatNI – a decentralized alternative to ChatGPT;
- Chat with Hal – a customized AI assistant.
These examples show that decentralized solutions can compete with tech giants’ products. Some in the community, including Andre Cronje, express skepticism about the symbiosis of AI and blockchain.
Network Architecture
Bittensor is a self-sufficient Layer 1 (L-1) blockchain. It uses the Substrateframework and Polkadot SDK. The network has undergone various updates since its launch:
- Kusanagi – first version released in January 2021 on the Polkadot parachain;
- Nakamoto – second version implemented through a hard fork in November 2021;
- Finney – existing network launched in March 2023 as an independent blockchain.
Bittensor has a notable feature: the use of Yuma, a hybrid consensus algorithm. It combines Proof-of-Stake and Proof-of-Work. The algorithm customizes AI model quality and protects the network from malicious validator activity.
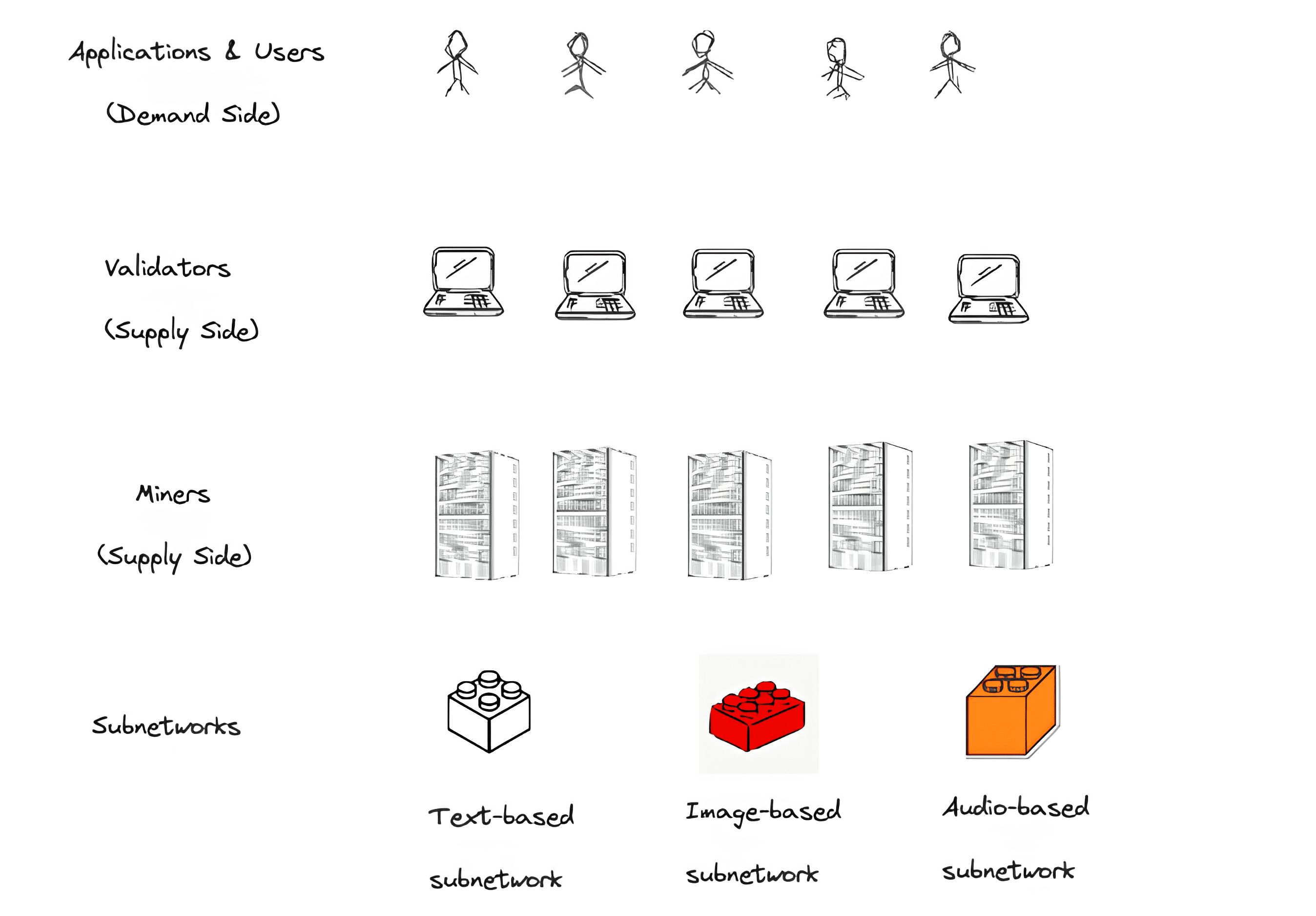
The blockchain consists of a few crucial participants, which include:
- miners that offer AI models. When a node starts, a miner’s AI algorithm processes and responds to user requests. It contributes to the PoW component of the consensus algorithm.
Bittensor doesn’t control miners’ resources or models. Miners perform all computations off-chain, making the infrastructure cost-effective. The AI provider handles training, network connection, and provides computing power;
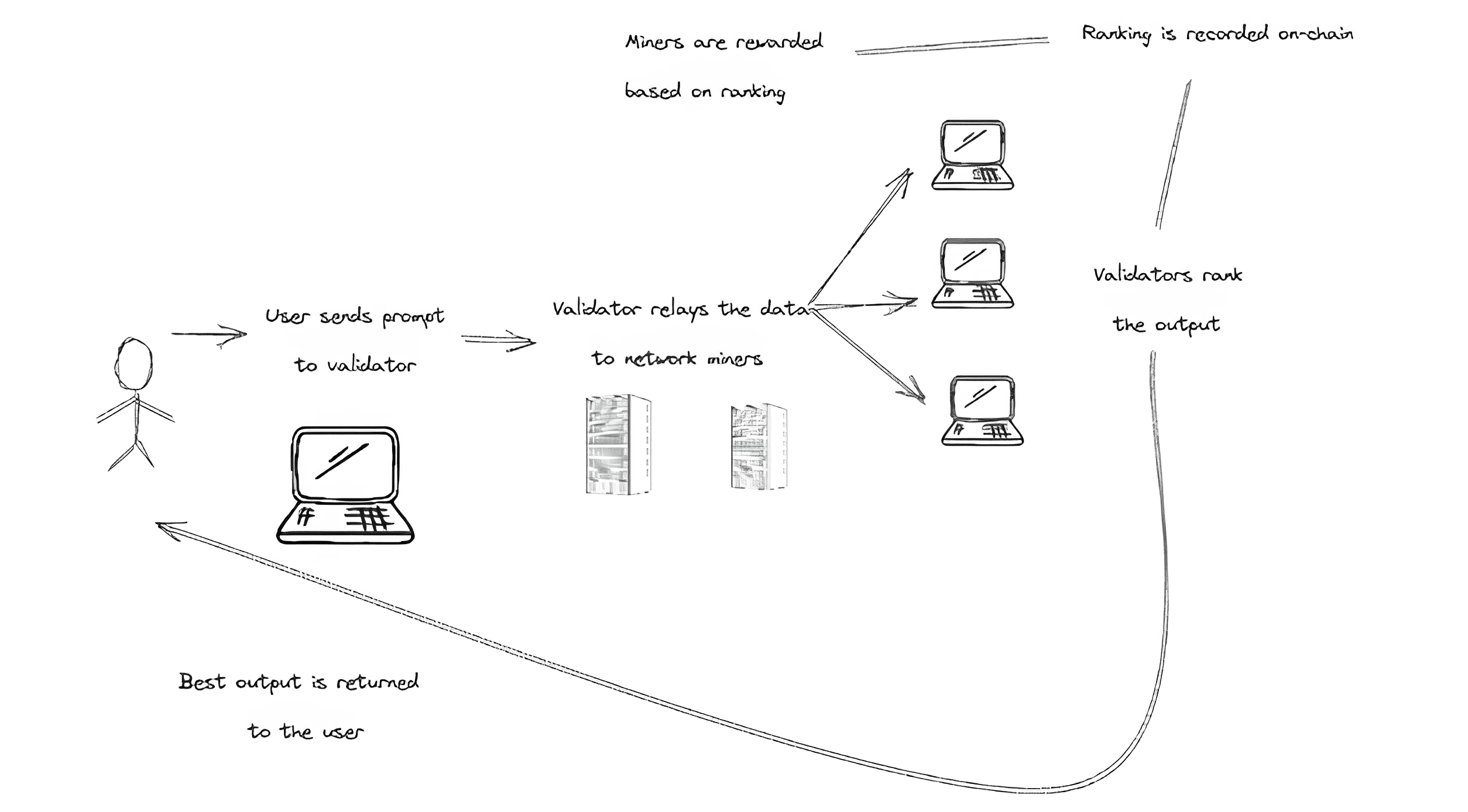
- validators send user requests to miners and assess their responses. A consensus algorithm ensures that validators align their opinions. Validators join the network by running individual nodes and locking TAO tokens, risking forfeiture in case of misconduct.
Mining company Foundry and Neural Internet, a decentralized autonomous AI research organization, stand as major validators for Bittensor;
- nominators, who are TAO holders, delegate their assets to validators through staking, increasing their influence in decision-making. In return, nominators receive a share of the validator’s income. Currently, TAOs stake is available at 16% per annum.
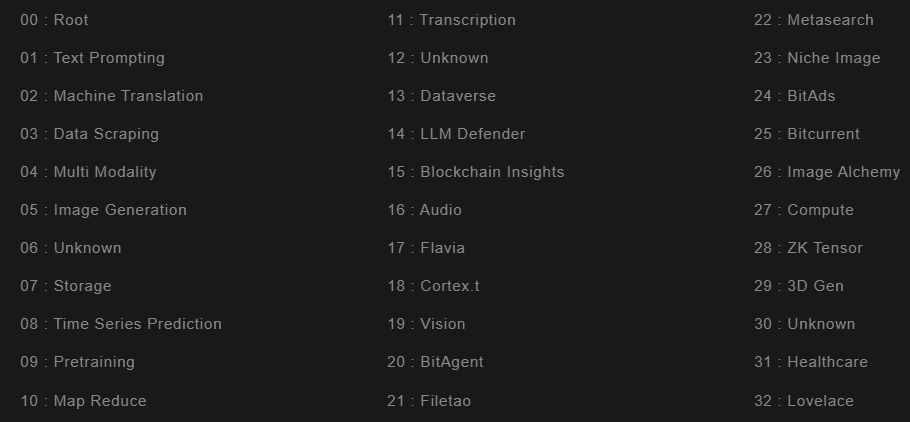
Bittensor comprises 32 subnets, each equipped with miners specialized for specific tasks. Validators from the root network assess the quality of the subnets, comprising the largest miners from each subnet.
MoE Concept
Creating artificial general intelligence (AGI) is the ultimate goal of the AI industry. AGI would have the ability to solve various tasks and learn in a flexible manner, like humans. But even technology giants with almost limitless resources find this goal extremely challenging..
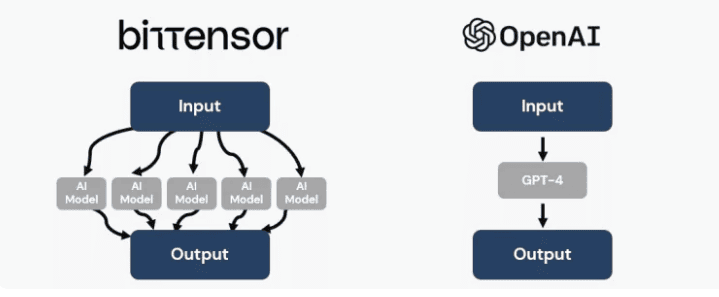
Bittensor employs the MoE (Mix of Experts) architecture as an alternative. This architecture comprises specialized AI models that handle user inquiries and provide the best responses from an expert, specifically, the most relevant algorithm.
In practice, Bittensor uses subnets to specialize in specific query groups. Users can register their subnets and pay a fee to hire AI algorithm providers for task completion. Participants receive 18% of the total revenue. It’s important to note that developers determine the maximum number of subnets, so Bittensor is not yet a fully open blockchain in this regard.
Currently, the Bittensor network comprises 32 subnets specializing in generative art, translation, text queries, and more.
Collaboration among experts is one of the benefits of MoE. It enables the development of a language-specific coding guide, for instance. In this setup, the text model manages the guide’s structure, the programming professional handles the coding, and the AI translator takes care of the necessary language.
MoE’s modular architecture enables a broader range of tasks compared to centralized algorithms. Furthermore, the addition of specialized sub-networks extends the capabilities of MoE.
Centralized products like ChatGPT may multitask, but their closed code raises uncertainty about whether they function as a monolithic ‘super algorithm’ or a set of specialized modules. If they function as modules, they lack inherent advantages over Bittensor. But if they operate as a monolithic ‘super algorithm’, the complexity and cost of training will increase with new directions, potentially making MoE a better solution in theory.
Cooperative Learning
The market for AI faces issues of fragmentation and a dearth of open-source culture. Developers may work on similar tasks as their peers, yet they still need to create their models from scratch. This leads to a situation where investments in training data and computing power are duplicated. Bittensor aims to solve this problem by utilizing the transparency of the blockchain.
The Yama consensus mechanism requires the validator to request all miners of the corresponding ‘specialization’ to get the most responses and check them. The evaluation result is then recorded on the blockchain and shared with the public. This ensures that miners are aware of:
- the query;
- the relative score of their answer.
Inefficient AI models can improve by evaluating the quality of their responses with this data.
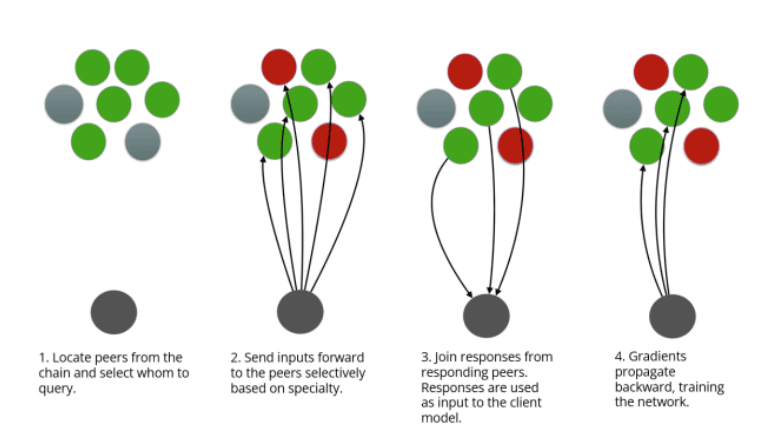
AI learning basics are similar, but in centralized products like ChatGPT, developers or users assess response accuracy.
In Bittensor, learning occurs, but it happens synchronously. Many algorithms evaluate simultaneously with each request, enhancing resource efficiency. This approach differs from competing centralized AI models, which need to learn on their own and may repeat errors, reducing efficiency.
It is important to note that Bittensor assists developers in improving their algorithms. The provider is responsible for creating and tuning parameters, conducting initial training, managing data storage, and providing computing power. This setup encourages healthy competition in the open market.
Reward System
Bittensor aims to motivate AI model providers by using the TAO cryptocurrency as a reward mechanism:
- the Bittensor network issues one TAO token when it finalizes a block (as of the time of writing);
- this token is then distributed among subnets based on coefficients. Each subnet has its parameter assigned by the validators of the root subnet;
- in a subnet, miners receive rewards based on the quality of their responses to user queries. The subnet validators check each miner’s response;
- validators also receive a reward for their work, although it is a bit lower than that of the miners.
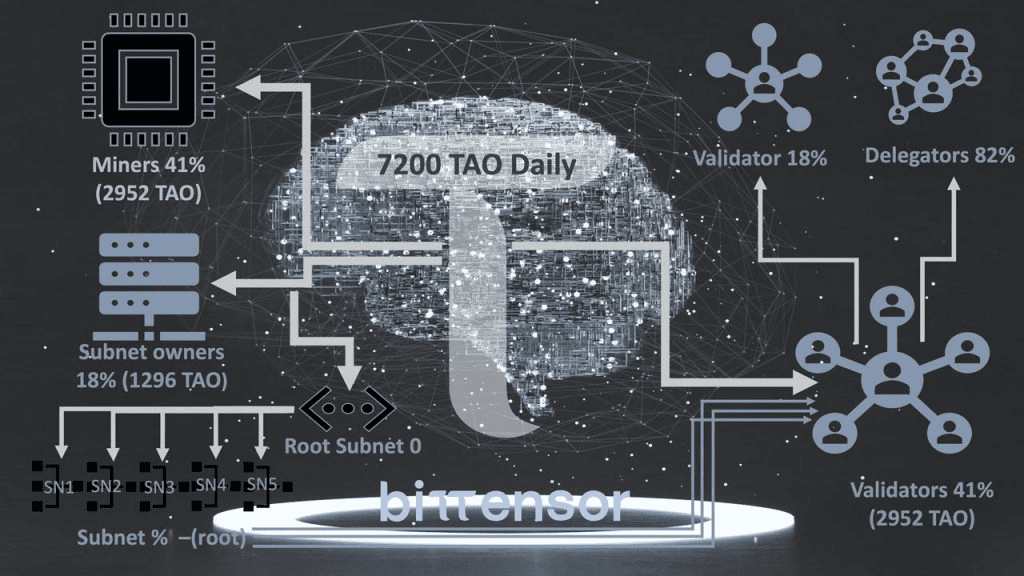
Bittensor follows the Bitcoin model of token mining to incentivize network participants. It’s worth noting that any subjective evaluations won’t factor into this analysis. Miners’ earnings in fiat currency and the profitability of maintaining AI algorithms depend on the popularity of Bittensor, the products built using it, and user demand for cryptocurrency to pay for requests.
On January 9th, the project team submitted the first proposal to enhance Bittensor, known as BIT001. The proposal seeks to establish autonomous staking pools and transfer the reward distribution authority from the validators of the root network to the members of specific subnets. Once the update is implemented, each subnetwork will have its token called Dynamic TAO (dTAO), and its value will vary based on user demand.
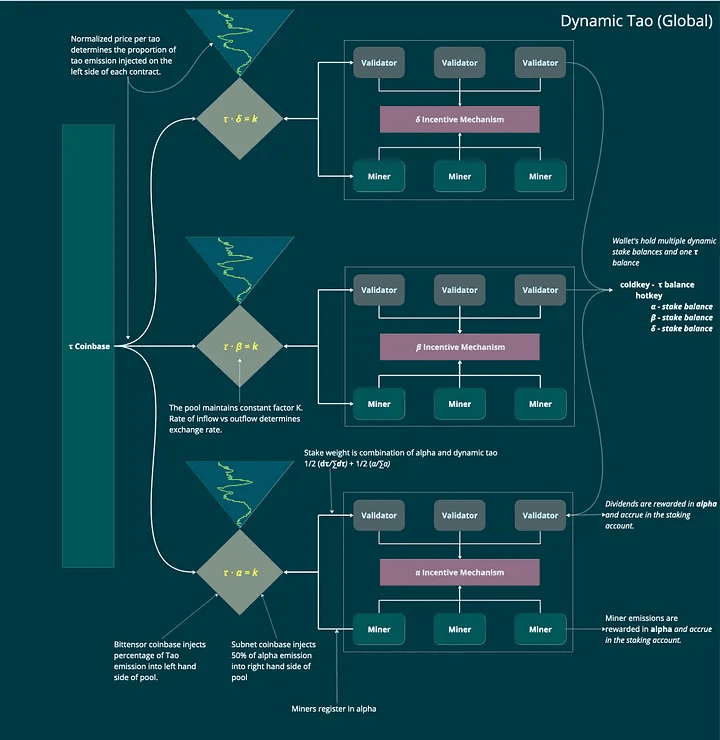
The new incentive mechanism allows users to influence issue allocation. They can do this by delegating assets to a validator of a specific subnetwork and increasing the weight of their vote.
What Bittensor Does NOT Do
Bittensor might seem like a decentralized AI model powered by miners, but it serves as a communication infrastructure for diverse AI algorithms. This facilitates their development and provides rewards. The project:
- does not aim to support or train AI models, as that is the responsibility of their owners, i.e. the miners. Bittensor has neither the technology nor the goal to engage in algorithm improvement. Still, the network offers response scores to assist models in enhancing their knowledge, addressing the problem of starting from scratch, and reducing costs for providers;
- does not create AGI, despite its resemblance to ‘super AI’ at the user level. The queries and responses move within specialized sub-networks and algorithms, and they are not broadcasted to all miners, preventing the training of a universal model.
Bittensor is building a decentralized marketplace that allows users to buy AI knowledge without relying on monopolies such as OpenAI.
TAO Cryptocurrency and Project Tokenomics
TAO serves multiple functions: financial incentives, facilitating consensus, managing projects, and paying fees. It is the primary currency for participating in the blockchain as a consumer, miner, or validator.
The project has unique tokenomics inspired by Bitcoin. This is uncommon for blockchain startups. The key features include:
- a total supply of 21 million TAO;
- no pre-mining occurs – miners generate all tokens while the network is running;
- the system issues one TAO every 12 seconds (block finalization time). As of now, miners have mined approximately 30% (6 million) of the tokens;
- Bittensor staking holds about 90% of the circulating supply of TAOs, one of the highest rates in the market. In comparison, Ethereum has around 25% of total ETH staked, and Solana has about 68% of SOLs staked;
- there is a halving of block mining rewards every 10.5 million blocks.
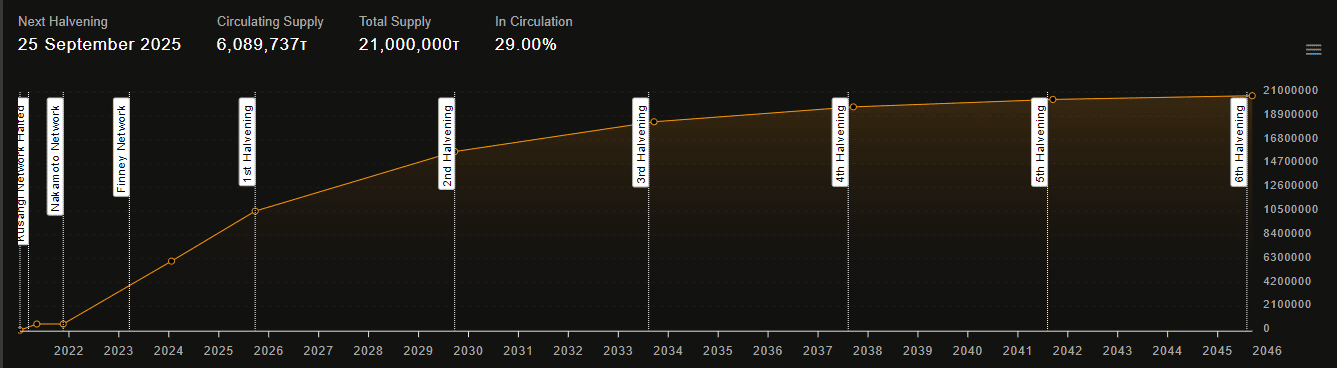
Bittensor has no treasury, locked investor shares, or funds for airdrops and other community incentives. The only recipients of tokens are miners and validators.
This reduces the possibility of attracting new users and developers through economic incentives and subsidy programs (which require more sources of funding). But it ensures full transparency and predictability of inflation.
It’s worth noting that there’s also no information about the project’s investors. Bittensor.org lists Polychain Capital and DCG as partners. Pitchbook reports that The Opentensor Foundation behind the project has completed an early investment round. No further details yet.
Conclusions
Many experts see the synergy between AI and blockchain as a promising trend for 2024. However, developers are still looking for a specific model to gain an edge over centralized solutions.
In the emerging field of crypto markets, Bittensor is a leading contender. The project team aims to establish a decentralized market for AI knowledge, providing new opportunities for model owners to monetize their efficiency, without revolutionizing AI algorithms.
Bittensor’s approach paves the way for other blockchain-based AI projects, like those concentrating on decentralizing computing resources or creating a fair market for training data.




